Moringa is a vegetable tree that is extremely nutritious and has many potential and healthy uses. The Moringa tree is believed by many to be the most giving plant in all of nature. It is loaded with nutrients, antioxidants and healthy proteins. Moringa is quite possibly the most amazing plant that anyone has ever studied.
Moringa Oleifera (Moringa) is called the Tree of Life because it is one a nature’s most nutritious foods. The powder in the Moringa leaf is containing over 90 nutrients and 46 antioxidants along with all of the essential amino acids.
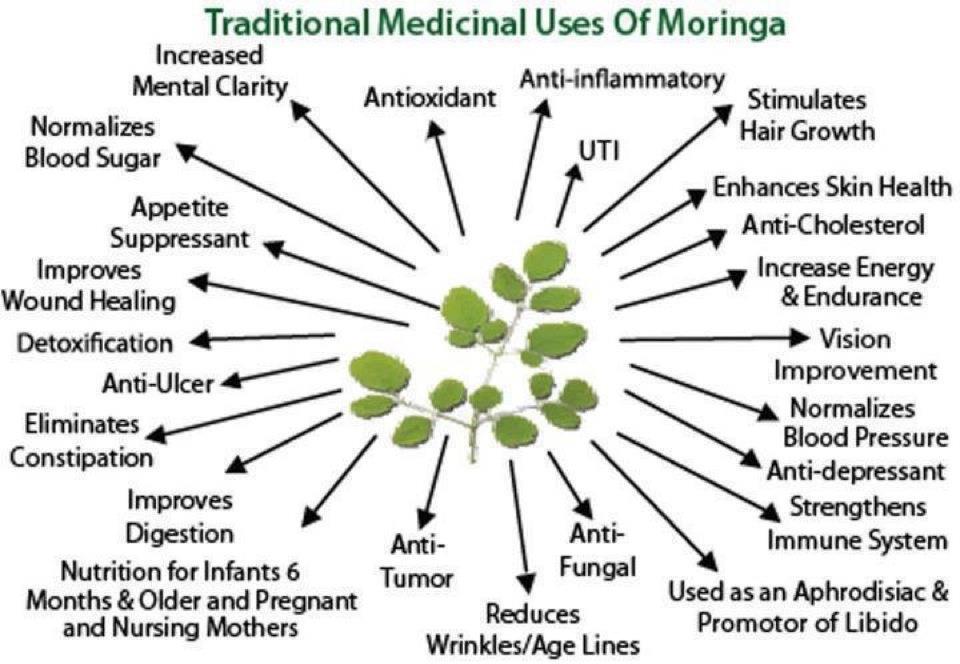
Increases the Natural Defenses of the body
Provides nourishment to the eyes and the brain.
Promotes metabolism with bio-available ingredients
Promotes the Cell structure of the body
Promotes natural Serum cholesterol.
Lowers the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
Promotes the normal functioning of the liver and the kidney.
Beautifies the skin
Promotes energy
Promotes proper digestion
Acts as an antioxidant
Takes care of the immune system of the body
Promotes healthy circulatory system
It is an anti-inflammatory
Gives a feeling of general wellness
Supports the normal sugar levels of the body.
Moringa leaf boosts your energy in a natural manner, and is a remarkable source of nutrition. This energy promotion does not happen because of sugar, so it is lasts for a long time. Individuals ingesting it say that their ulcers are healed, tumors restricted, there are reduction in the arthritis pains and inflammations, controlled blood pressure, the skin problems are restored, and finally they have stronger defenses against diseases.
Another property of the Moringa leaf is its soothing ability, because of which it can lower the blood pressure and promotes good sleep. It can also purify water since it has a detoxifying effect. Also a coagulant agent, Moringa can attach itself to hazardous bacteria and other materials, a process that is surmised to occur in the body too. The happy outcome is more sustained energy without any over-activity, balanced hormone and gland system, controlled blood pressure, and a rested nervous system.
Modern research has found that Moringa leaves, as well as other parts of the tree, have been used since ancient times as traditional ayurvedic medicine in several cultures such as a natural antibiotic, an aid in childbirth, for treating liver disorders and many other uses. Moringa has been used for inflammation, malnutrition, wounds, diabetes, iron deficiency, high blood pressure and other conditions.
Containing over 90 nutrients and 46 antioxidants, Moringa (Moringa Oleifera) is one of nature’s most nutritious foods. Ideal for helping our bodies maintain optimum health. Moringa leaves are highly nutritious and are rich in vitamins K, A, C, B6, Manganese, Magnesium, Riboflavin, Calcium, Thiamin, Potassium, Iron, Protein and Niacin. Ounce for ounce, Moringa contains seven times the Vitamin C found in oranges, four times the beta carotene of carrots, three times the iron of spinach, 14 times as much calcium as milk and three times the potassium of bananas. Moringa also contains all 8 essential amino acids and is rich in flavonoids, including Quercetin, Kaempferol, Beta-Sitosterol, Caffeoylquinic acid and Zeatin. Moringa is sometimes referred to as the “Miracle Tree” because all parts of the plant are edible and medicinal. It can also thrive in tough climates and poor soil. Its combination of high nutrition, sustainability and hardiness has caused it to be promoted widely in Africa to help fight hunger, malnutrition and disease.
Moringa Contains Very High Antioxidants and Anti-inflammatory Compounds.
Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds work best when combined with other antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents. Nature allowed for a better efficacy when combined, a synergy of the compounds being much more effective than a single compound. Moringa contains the following antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds or compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory characteristics.
Antioxidants:
Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, Vitamin B (Choline), Vitamin B1 (Thiamin), Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (Niacin), Vitamin B6, Alanine, Alpha-Carotene, Arginine, Beta-Carotene, Beta-sitosterol, Caffeoylquinic Acid, Campesterol, Carotenoids, Chlorophyll, Chromium, Delta-5-Avenasterol, Delta-7-Avenasterol, Glutathione, Histidine, Indole Acetic Acid, Indoleacetonitrile, Kaempferal, Leucine, Lutein, Methionine, Myristic-Acid, Palmitic-Acid, Prolamine, Proline, Quercetin, Rutin, Selenium, Threonine, Tryptophan, Xanthins, Xanthophyll, Zeatin, Zeaxanthin, Zinc.
Anti-inflammatory compounds:
Vitamin A, Vitamin B1 (Thiamin), Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Arginine, Beta-sitosterol, Caffeoylquinic Acid, Calcium, Chlorophyll, Copper, Cystine, Omega 3, Omega 6, Omega 9, Fiber, Glutathione, Histidine, Indole Acetic Acid, Indoleacetonitrile, Isoleucine, Kaempferal, Leucine, Magnesium, Oleic-Acid, Phenylalanine, Potassium, Quercetin, Rutin, Selenium, Stigmasterol, Sulfur, Tryptophan, Tyrosine, Zeatin, Zinc.
The Essential Amino Acids of Moringa and Briefly Explain Their Importance for Human Health.
Histidine - Moringa leaves contain histidine, a semi-essential amino acid - adult generally produce adequate amounts but children usually may not. It is believed that histidine may increase the body resistance to environmental toxins and allergens (factors that trigger allergies in susceptible persons). Since histidine found abundantly in hemoglobin - the respiratory pigment protein needed for oxygen transportation to every cell – histidine aids in the prevention of anemia.
Histidine is also a mild vasodilator and helps increase blood circulation. According to some research, people with rheumatoid arthritis have low levels of histidine; therefore it has been used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A deficiency of histidine can also cause poor of hearing. Since histidine is found in numerous proteins, its presence is needed for normal general physiology.
Isoleucine - Moringa contains isoleucine in large amounts. Its main role in the body is related to its incorporation into many proteins and enzymes. This is one of the essential amino acids needed for hemoglobin formation, as is histidine. Therefore, its presence is useful for the prevention or treatment of anemia. Isoleucine plays a role in optimal growth during childhood;babies and children need much more isoleucine per body weight than adults! It also maintains normal blood sugar and energy levels and therefore it is particularly important for diabetics. Isoleucine is metabolized in muscle tissue and can enhance energy levels and increase endurance. Athletes and everyone exercising regularly need extra isoleucine.
Leucine - This is another essential amino acid related to isoleucine and valine, all vital for normal growth in children. Moringa contains large amounts of leucine as well. These three amino acids work together to protect muscles, build muscles, and enhance energy levels and stamina. They also promote bone, skin and muscle tissue healing and therefore are recommended for those recovering from injuries, stress or surgery.Leucine may help to lower elevated blood sugar levels, which is important for diabetics. For normal growth, small children and babies need much more leucine per body weight than adults. Leucine also aids in increasing growth hormone production.
Lysine - Lysine is required for normal growth and development in children, who need vast amounts of this amino acids. Although plant sources are usually poor in lysine.Moringa leaves are quite rich in this essential amino acid. Lysine helps calcium absorption and bone development, and maintains proper protein balance. Lysine also aids in the production of antibodies[ protective proteins of the immune system], hormones and enzymes, in skin maintenance and formation, and tissue repair .Since it helps to build muscle protein, lysine is necessary for those recovering from stress, injuries and surgery. In people with “bad” serum fats and high cholesterol, lysine lowers high serum triglyceride levels.
Another useful quality of lysine is its capacity to inhibit the multiplication of viruses, especially herpes viruses.
Methionine and Cystine - These are important sulfur-containing amino acids. Cystine is the stable form of the sulfur-containing amino acid cysteine. The body readily converts one into the other as needed, therefore the two forms can be considered as a single amino acid in metabolism. Sulfur-containing amino acids are involved in detoxification of the organism; they help to neutralize and eliminate harmful toxins and protect the body against radiation damage caused by UV rays and x-rays .They are free radical destroyers, and work best when taken with selenium and vitamin E ( see "Antioxidants in Moringa" ). Cystine helps to protect the river and brain from damage due to toxics such as alcohol , drugs, and environmental pollutants.
Methionine and cystine are main constituents of the proteins of fingernails, skin and hair; they promote proper elasticity and texture of the skin and hair. Ladies, real beauty comes from the inside, and sulfurcontaining amino acids must surely be ingredients of any diet that fights skin aging!
Cystine may have anti-inflammatory properties that can be helpful in the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Cystine and metheonine are recommended to be supplemented in the treatment of some forms of cancer. These two amino acids also promote wound healing; therefore they are helpful after surgery and burns. They are known to bind iron, aiding in iron absorption. For those interested in losing weight, it is worth mentioning that cystine also promotes the burning of fat and the building of muscle.
Phenylalanine and Tyrosine - These two essential amino acids, well represented in Moringa leaves, are particularly important for the health of the central nervous system. Once in the body, phenylalanine can be converted into tyrosine, which in turn is used to synthesize two key brain transmitters that promote alertness: dopamine and norepinephrine. These two amino acids – phenylalanine and tyrosine – can therefore elevate mood, decrease pain, help with memory and even suppress appetite.
Phenylalanine and tyrosine should be supplemented in the treatment of depression, arthritis, obesity and Parkinson’s disease. Phenylalanine is effective for controlling pain, especially the chronic pain in osteoarthritis and rheumatoids arthritis, according to some studies. Similar to other amino acids, these two are incorporated in a variety of proteins throughout the body.
Threonine - Threonine is also very well represented in Moringa, although its content is usually low in many grains and other plant protein sources. This amino acid is important for the formation of collagen and elastin, two main proteins of the skin. It also helps to protect the liver and has a lipotropic function (against fatty liver). Threonine is present in high concentrations in the heart, central nervous system and skeletal muscle. It maintains their health and normal functions. It also enhances the immune system by aiding in the production of antibodies, and promotes thymus (a gland vital for the function of the immune system) growth and related activity. Other vital nutrients are also better absorbed when threonine is presen in the food. Some use threonine supplements in certain cases of depression. Infants need much more (8 times) threonine per body weight than adults.
Tryptophan- An essential amino acid, tryptophan is required for the production of niacin ( vitamin B3) and serotonin (the neurotransmitter involved in relaxation and sleep) among others. Therefore, tryptophan helps to control depression and insomnia, stabilizes emotional moods, and it also eases perception of pain, and might combat inflammation. It also aids to control hyperactivity in children and alleviates stress. Although tryptophan is the rarest of all amino acids to be found in protein’s composition, it plays an important role in reducing stress-related mood disorders, and helps relaxation and good sleep! We all need some extra tryptophan sometimes! Supplements of tryptophan are not approved in the USA, so, when needed, we have to get it from food. Moringa is an excellent plant source of tryptophan, and its concentration in the leaves exceeds the concentration in soy beans. Since some migraine sufferers have abnormally low levels of tryptophan, it is believed that tryptophan can also ease the pains as sociated with certain types of migraines.
Valine - unlike tryptophan, valine has a stimulant effect. It is needed for muscle metabolism and structure, general tissue repair and the maintenance of a high concentrations in muscles, similar to related amino acids, isoleucine and leucine. These three branched-chain amino acids can be used as an energy source by muscle tissue, thus preserving the use of glucose and supplying stamina. Studies have shown that these amino acids are useful in restoring muscle mass in people with liver disease, or after physical stress, injuries and surgery. Moringa leaves are at least as rich (if not more) as soy beans (and soy protein concentrate) in valine.
Moringa is one of the very few plant sources that contain all 9 essential amino acids.
Moringa’s essential amino acids presence and digestibility are as good as soy (one of the best protein sources). Soy is often a highly processed product while Moringa is presented in its natural state.
Moringa’s essential amino acids presence and digestibility are better than those required by the standards of WHO, FAO and UNO. Moringa, even in small portions, provides adequate amounts of protein nutrients for everyone, including healthy or medically compromised individuals, children, senior adults, lactose intolerant individuals, vegetarians and people with soy allergies.
Amino Acid Content of Moringa
All values are per 100 grams of edible portion.
Fresh Leaves Dried Leaves
Arginine 406.6 mg 1,325 mg Histidine 149.8 mg 613 mg Isoleucine 299.6 mg 825 mg Leucine 492.2 mg 1,950 mg Lysine 342.4 mg 1,325 mg Methionine 117.7 mg 350 mg Phenylalinine 310.3 mg 1,388 mg Threonine 117.7 mg 1,188 mg Tryptophan 107 mg 425 mg Valine 374.5 mg 1,063 mg